The digital age revolves around one key concept: computer networks. These intricate webs connect our devices, allowing information to flow freely, from browsing websites to playing online games. But how does it all work? This guide unravels the mysteries of computer networks, making them easier to understand for CBSE Class 12 students.
The Building Blocks: Network Components
Imagine a network as a bustling city. Devices like your phone or laptop are the residents, and connections are the roads. Here's a breakdown of the key players:
- Devices: These are the gadgets that connect to the network, like your computer, smartphone, printer, or even smart TV. They act as the senders and receivers of information.
- Connections: These are the pathways that data travels on, similar to roads in a city. Common connections include Wi-Fi (wireless) and Ethernet cables (wired).
- Network Interface Card (NIC): This chip resides within your device, allowing it to connect to the network and translate data into a transmittable format.
- Routers: Think of routers as traffic controllers. They direct data packets (pieces of information) to the correct device within the network or send them out to the wider internet.
- Switches: These devices connect multiple devices within a network, ensuring smooth communication between them.
Network Types: Size Matters
Networks come in various sizes, each catering to specific needs. Here are the main types you'll encounter:
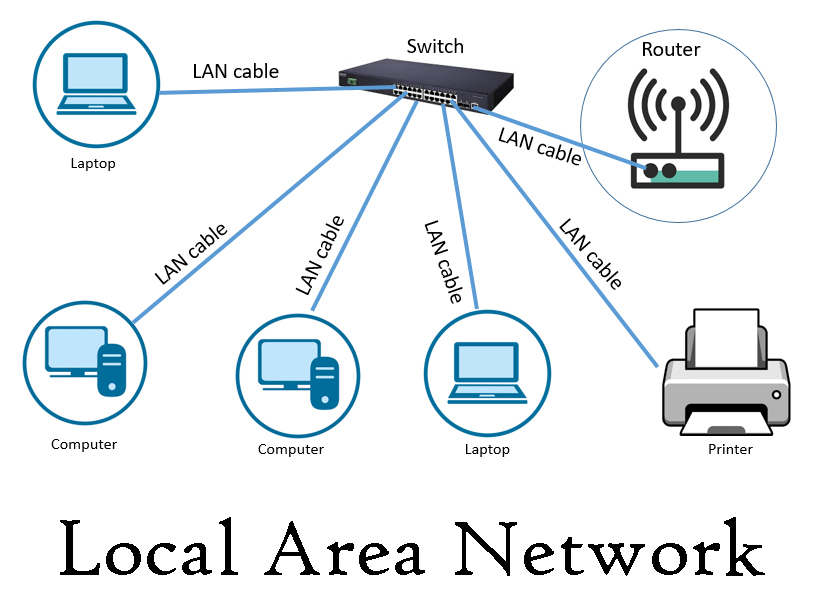
- Local Area Network (LAN): This is the network you're probably most familiar with. It connects devices in a limited area, like your home or school, enabling them to share resources like printers and files.
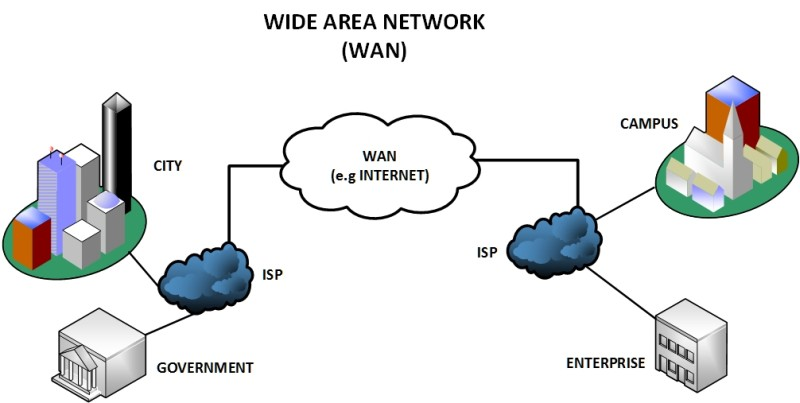
- Wide Area Network (WAN): WANs span vast geographical distances, connecting LANs across cities, countries, or even continents. The internet itself is a prime example of a WAN.
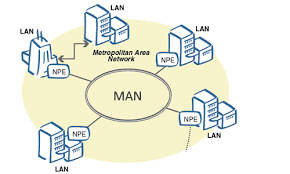
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): As the name suggests, MANs cover a larger area than a LAN, typically encompassing a city or metropolitan region. They offer high-speed connectivity for organizations and institutions.
- Personal Area Network (PAN): PANs are tiny networks connecting devices within a person's immediate surroundings. Think of connecting your Bluetooth headphones to your phone.
Functionalities: Why We Network
- Resource Sharing: Networks enable devices to share resources like printers, scanners, and storage space, maximizing efficiency.
- Communication: We can exchange information through emails, messages, video calls, and online collaboration tools, all thanks to networks.
- Entertainment: Streaming movies, music, and online games rely heavily on robust networks to deliver content seamlessly.
- Information Access: The internet, a giant network of networks, provides access to a vast amount of information at our fingertips.
Conclusion :
Understanding computer networks is like understanding the language of the digital world. By grasping the basic components, network types, and functionalities, you'll be better equipped to navigate the ever-evolving digital landscape. Now that you're armed with this knowledge, dive deeper and explore the fascinating world of network protocols, security measures, and emerging network technologies!